
 Xingaonai
Xingaonai
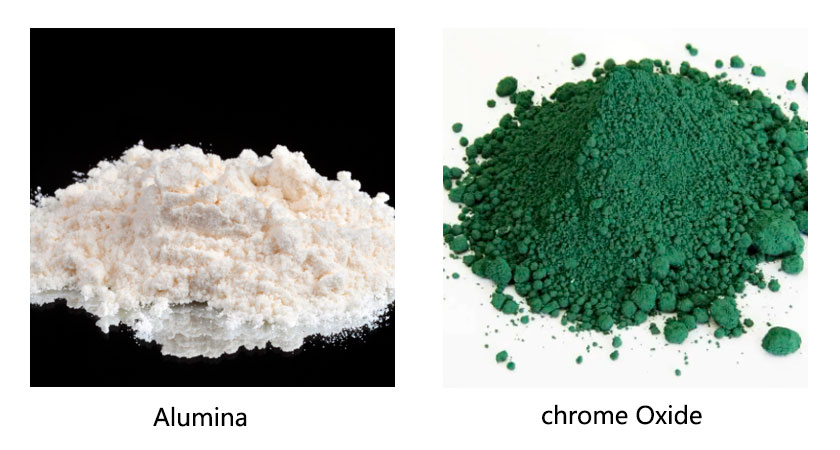

Alumina is an inorganic compound with high melting point, high hardness, and amphoteric oxide characteristics. Alumina is generally white powder and invisible, with boiling point and melting point at 2980℃ and 2050℃ respectively. It is not easily soluble in water, but soluble in strong acid and strong alkali. In nature, alumina mainly exists in the form of bauxite, which is extracted from bauxite by sintering and other processes.
Alumina-and-chrome-Oxide.html">Chrome Oxide is also an inorganic compound with high strength, wear resistance and corrosion resistance. It is generally green crystalline powder with dark green and metallic luster, belonging to hexagonal system or amorphous crystal. The boiling point and melting point of Chromium oxide are 4000°C and 2435°C respectively, and it does not fuse with alcohol and water. In nature, chromium oxide exists attached to ores such as chromite and chrome green iron ore.
Aluminum oxide is generally white powder, not easy to water, amphoteric oxide with high melting point, and reacts with acid and alkali.
Chrome Oxide is generally green powder and not easily soluble in water. Chromium oxide is an alkaline oxide that only reacts with acid.

Aluminum oxide has high hardness and poor hygroscopicity, and is often used in wear-resistant materials. The crystal structure is stable and has high temperature resistance. Chromium oxide has relatively low hardness, but has good corrosion resistance. Moreover, chromium oxide does not change color at high temperatures, which makes it unique.
Both aluminum oxide and chrome Oxide have good corrosion resistance, but they have different performances in different environments. Aluminum oxide has poor corrosion resistance to strong acids, but has good corrosion resistance to alkaline solutions. Chromium oxide has good corrosion resistance to both strong acids and strong alkalis, especially under high temperature conditions, where chromium oxide has more advantages.
Aluminum oxide has good high temperature resistance, can maintain stability above 1450°C, and has good corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, and insulation performance at high temperatures. Chromium oxide is also a good high-temperature resistant material. It can maintain stability and original performance under high temperature conditions. For example, at 1000-1200℃, the mechanical strength and chemical stability of chromium oxide can maintain good conditions.
Aluminum oxide has the characteristics of high melting point and high hardness. It is widely used in the manufacture of ceramics, refractory materials, abrasives, etc., and is used as a material for circuit substrates in the electronics industry.

chrome Oxide is mainly used for chromium carbide and smelting of metallic chromium. It is widely used in coloring agents such as ceramics, artificial leather, enamel, and catalysts for organic compounds.
Aluminum oxide is mainly prepared by sintering and Bayer process.
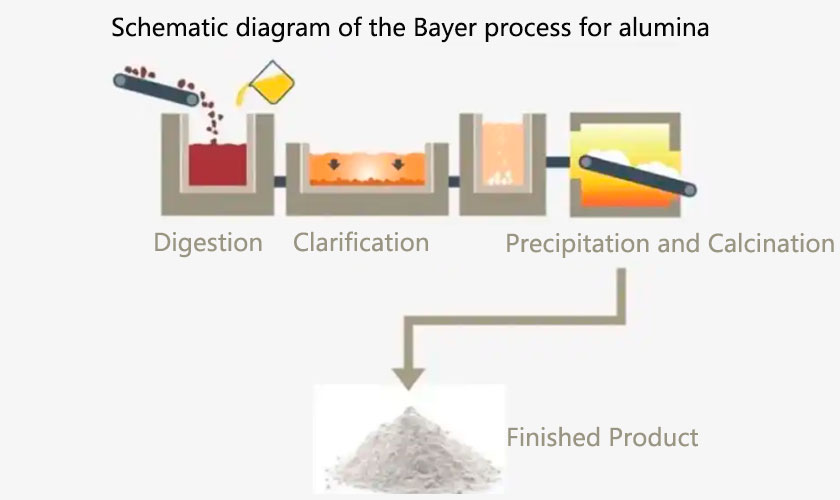
The Bayer process mainly dissolves bauxite, then parses aluminum hydroxide, and finally calcines at high temperature to obtain alumina.
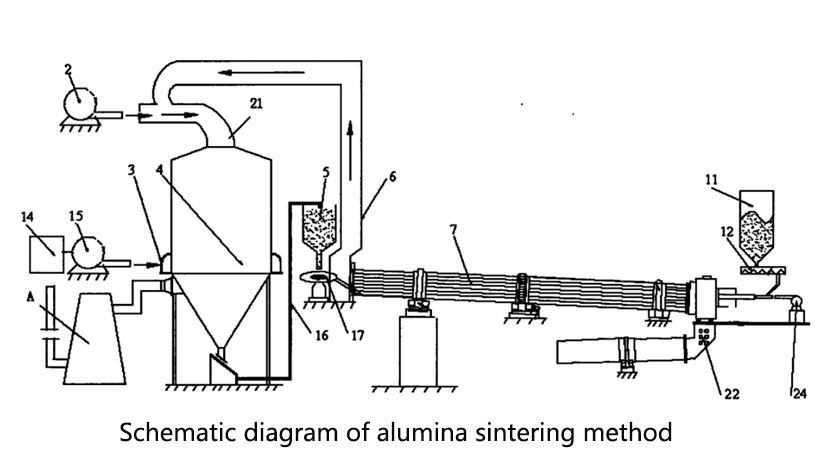
The sintering method is mainly to sinter after mixing sodium carbonate and bauxite, and then extract alumina through dissolution, filtration, precipitation, calcination and other steps.
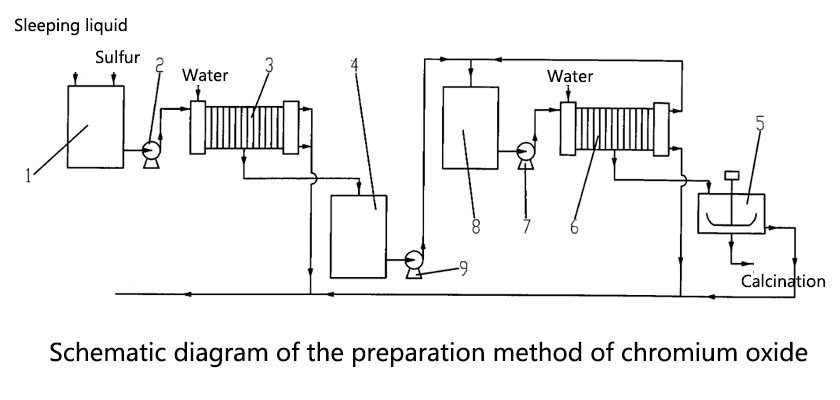
The preparation methods of chrome Oxide and aluminum oxide are very different. They are mainly obtained by reducing chromate or thermal decomposition of chromate.
In general, alumina and chromium oxide differ in chemical properties, physical properties, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance, uses and preparation methods. Only when we better understand their differences can we better utilize their value and make great contributions to industrial and social development.
Author: Xingaonai
Reprint address: https://www.xgncrusher.com/Industralnews/Difference-Between-Alumina-and-chrome-Oxide.html
Copyright © 2016-2030 Xingaonai Group All Rights Reserved. Xingaonai Sitemap